Differentiation Implicit Kappa Maths Resources for A Levels & GCSE Maths
An A Level Maths Revision tutorial on finding the differential using implicit differentiation of a function that is defined implicitly. https://ALevelMathsRevision.com

Implicit Differentiation Edexcel A level Maths Exam Questions Teaching Resources
What is implicit differentiation? An equation connecting x and y is not always easy to write explicitly in the form y= f (x) or x = f (y) However you can still differentiate such an equation implicitly using the chain rule: Combining this with the product rule gives us: These two special cases are especially useful:

Implicit Differentiation ALevel Maths Exam Question Walkthrough Tutorial AQA/Edexcel Exam
University of Leeds - MSc Mathematics. January mocks on the horizon? Kick-start your revision with our 2-day online Mock Preparation courses. Statistics 3rd, 4th, 5th, Pure 2-3rd, 5-6th and Mechanics 3rd, 4th, 5th January. Book your place now! This topic is included in all papers for AS-level and A-level OCR (MEI) Maths.

A2 Differentiation Implicit Differentiation Part 2 alevelmathematicsnotes
Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the Implicit Differentiation section of the Derivatives chapter of the notes for Paul Dawkins Calculus I course at Lamar University.

Implicit Differentiation AQA A level Mathematics YouTube
Watch Solution Did this page help you? FREE Maths revision notes on the topic: Differentiation. Designed by expert SAVE MY EXAMS teachers for the AQA A Level Maths: Pure exam.
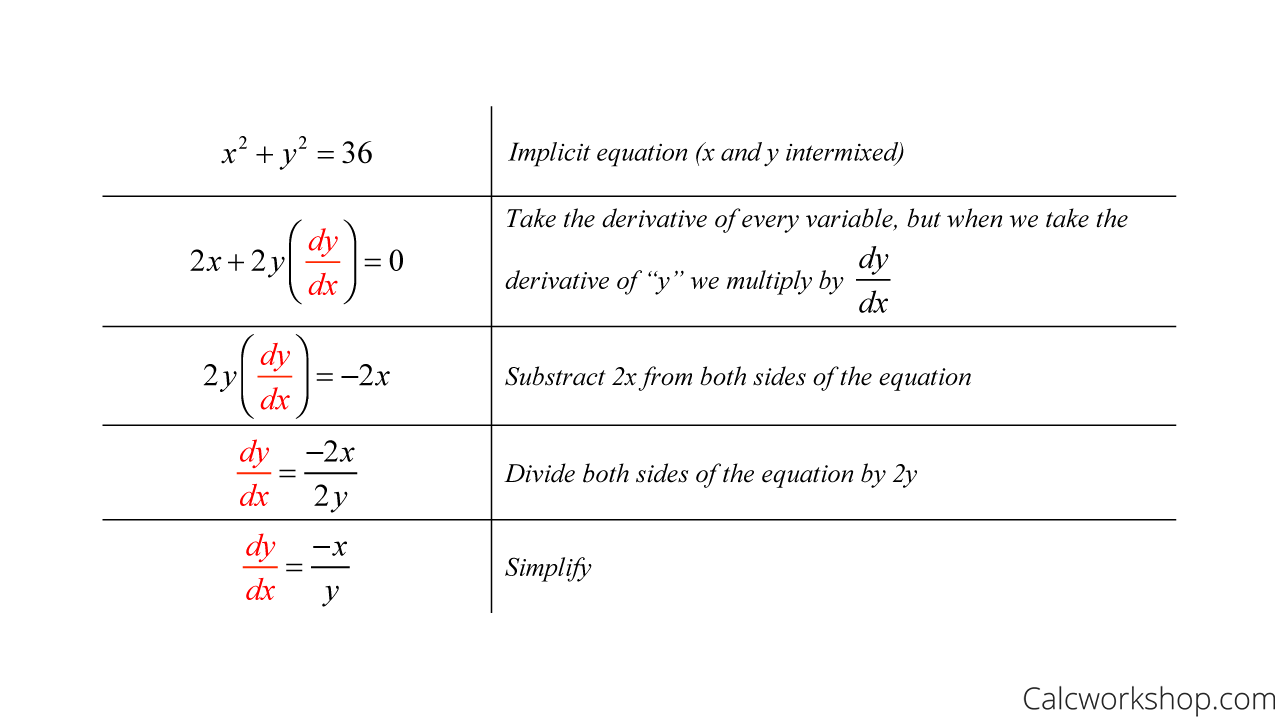
Implicit Differentiation (w/ Examples And Worksheets!)
Past paper questions for the Implicit Differentiation topic of A-Level Edexcel Maths.

A2 Differentiation Implicit Differentiation Part 1 alevelmathematicsnotes
Implicit Differentiation. If y 3 = x, how would you differentiate this with respect to x? There are three ways: Method 1. Rewrite it as y = x (1/3) and differentiate as normal (in harder cases, this is not possible!) Method 2. Find dx/dy: dx = 3y 2. dy.
Implicit differentiation, product rule, Integration, additional maths maths, A Level maths YouTube
Pure Maths Revision - Implicit Differentiation. Maths revision video and notes on the topic of implicit differentiation.

Differentiation (2) Implicit Differentiation (C4 Maths ALevel) YouTube
Implicit Differentiation is needed when a function is not explicitly written as (y = f (x)). It involves differentiating each term separately and then simplifying. This is often essential when dealing with curves and shapes defined by implicit functions. Everything you need to know about Implicit Differentiation for the A Level Mathematics AQA.

A Level Maths Notes A2 Differentiation Implicit Differentiation Part 3
A-Level Maths: G5-02 Differentiation: Introducing Implicit Differentiation TLMaths 118K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed Like Share 77K views 5 years ago A-Level Maths G5: Implicit.

Calculus Implicit Differentiation YouTube
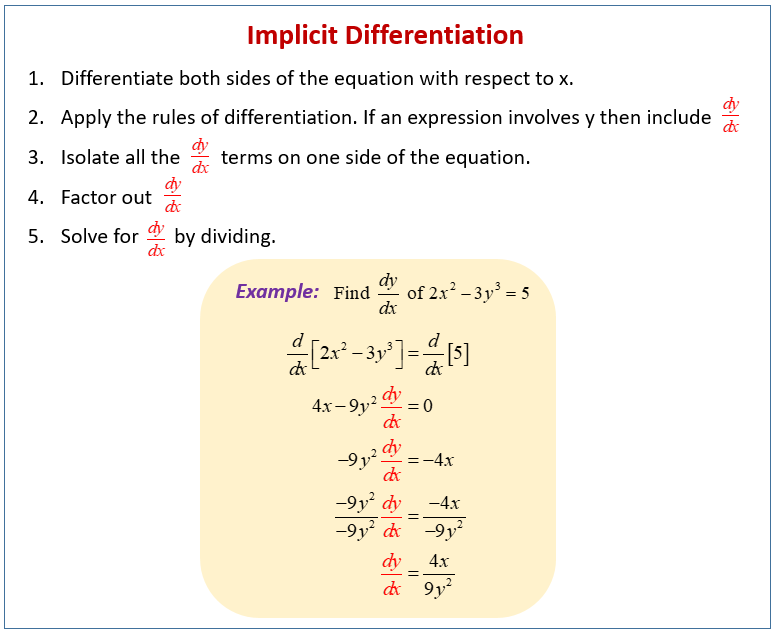
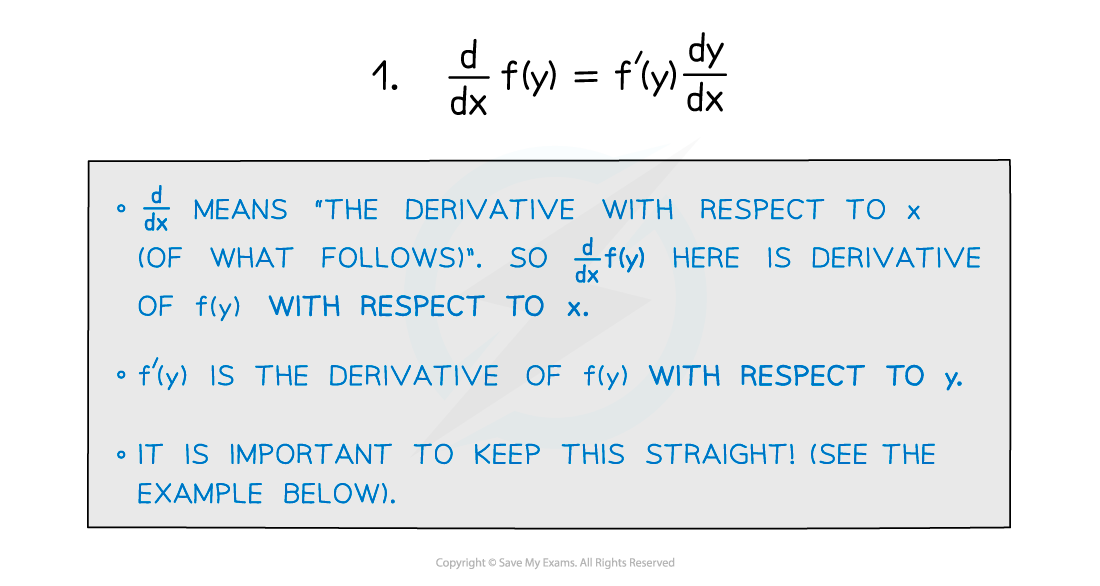
Step 1: Differentiate terms that are in x x only. Step 2: Use the chain rule to differentiate terms in y y only. \dfrac {d} {dx} (f (y))=\dfrac {d} {dy} (f (y))\dfrac {dy} {dx} dxd (f (y)) = dy d (f (y))dxdy This is the same as differentiating f (y) f (y) normally then multiplying by \dfrac {dy} {dx} dxdy.
Examples using Implicit Differentiation (solutions, formulas, videos)
Some relationships cannot be represented by an explicit function. For example, x²+y²=1. Implicit differentiation helps us find dy/dx even for relationships like that. This is done using the chain rule, and viewing y as an implicit function of x. For example, according to the chain rule, the derivative of y² would be 2y⋅ (dy/dx).
CIE A Level Maths Pure 3复习笔记4.2.1 Implicit Differentiation 翰林国际教育
Implicit Differentiation in a Snap! Unlock the full A-level Maths course at http://bit.ly/2oWggZo created by Lewis Croney, Maths expert at SnapRevise.SnapRev.

Differential of x=ln(sec2y) using Implicit Differentiation A Level Maths YouTube
A curve has implicit equation x y y y x xy3 3 2+ + + − = +3 3 6 50 2 . Find an equation of the normal to the curve at the point P(4,2). x y= 2 Question 6 A curve is described by the implicit relationship 4 3 21x xy y2 2+ − = . Find an equation of the tangent to the curve at the point (2,1). 4 19 42y x+ =

Implicit Differentiation Alevel Maths OCR, AQA, Edexcel YouTube
An implicit equation is an equation which is not in the form , it consists of two variable x and y which cannot be separated. Implicit Functions are differentiated by using "chain rule" in combination with the "product and quotient rule". When we differentiate y we write with the derivative i.e

A2 Differentiation Implicit Differentiation Part 3 alevelmathematicsnotes
What is implicit differentiation? An equation connecting x and y is not always easy to write explicitly in the form y= f (x) or x = f (y) However you can still differentiate such an equation implicitly using the chain rule: Combining this with the product rule gives us: These two special cases are especially useful: