Different Adaptations For A Camel That Helps Them To Survive / Adaptations are any behavioral or
The Camel (also known as the Dromedary Camel, the Arabian Camel, and the One-Humped Camel) is a large hoofed animal that is most commonly found in the hot deserts of Northern Africa and the Middle East. Because of the camel's resilience and adaptation to some of the harshest environments in the entire world, man domesticated camels thousands.

Adaptations in camels 5.10 a
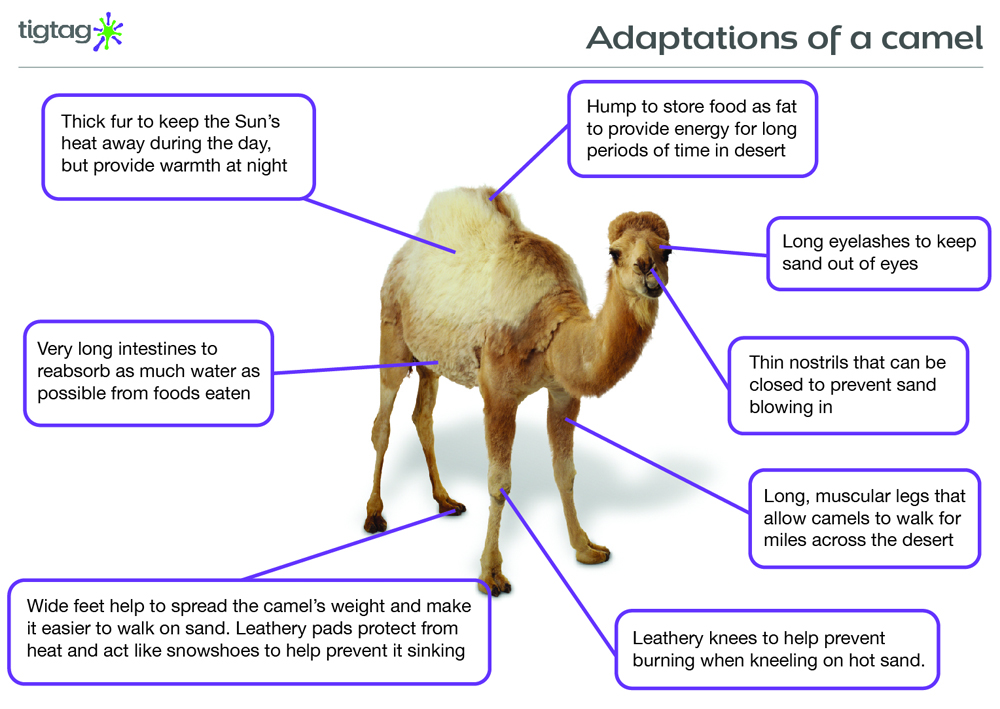
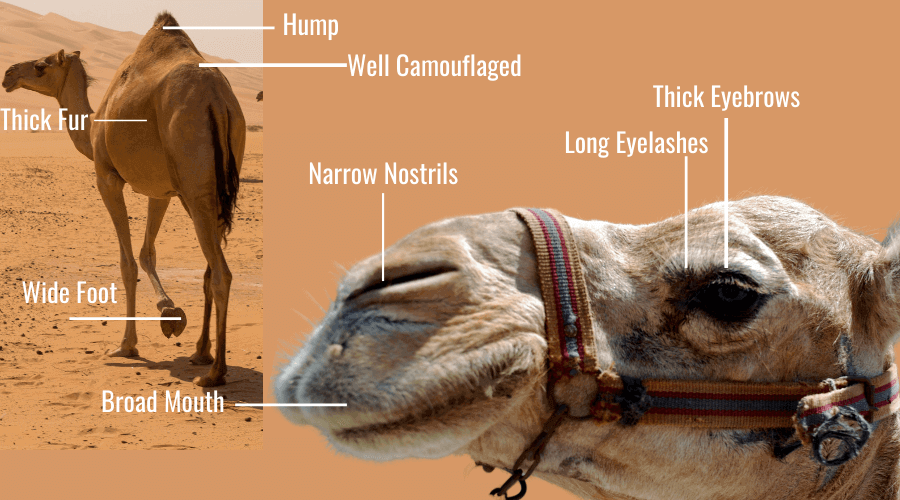
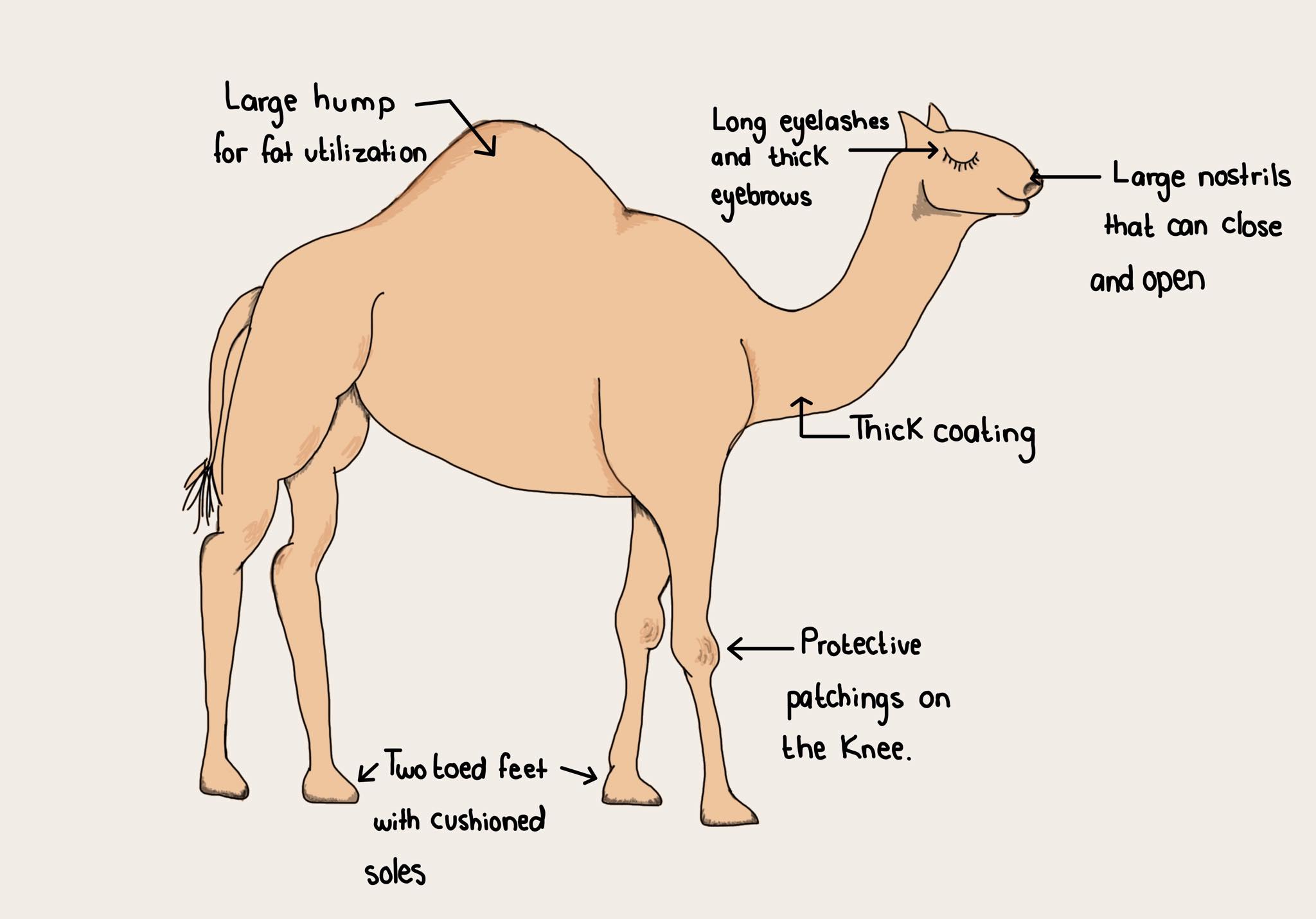
Adaptive traits can improve an animal's ability to find food, make a safer home, escape predators, survive cold or heat or lack of water. The camel has many adaptive traits for their life in the desert. They have wide feet for walking in sand. They have long eyelashes and thin, slit nostrils that they can close to protect them from blowing sand.

Camel adaptations YouTube
Camels can survive in the desert thanks to their amazing adaptations. Their fur keeps them cool, hump provides food and water, eyelashes keep the sand away, webbed feet enable walking on burning desert sand, and sweat glands help reduce heat. No wonder they are referred to as ships of the desert and worth so much.
Structural And Behavioral Adaptations Of A Camel This conserves energy and keeps them cooler
Camels are adapted to survive in arid and semi-arid climates with limited water resources and high temperatures. Their habitat also includes a variety of terrains, from sandy deserts to rocky mountains and grasslands. Here are some specific details about the climate and land where wild camels can be found: Climate:

Adaptation Camels
Camels are well suited to their desert habitats, with numerous clever adaptations that help them to tolerate extreme hot and cold environments. Camels are part of a group known as camelids. This makes them close relatives of llamas, alpacas, guanacos and vicuñas, which are all native to South America.

camel adaptation diagram help me our I willbmark u as a brainliest Brainly.in
July 11, 2022 by Wildlife Informer Camel adaptations to their habitat are essential for their survival. They have a number of physical and physiological adaptations that enable them to live in harsh weather conditions and survive on limited resources.

10 Camel Adaptations (Evolutionary Secrets!) Fauna Facts
Specially Adapted Digestive System Camels can go for long periods without drinking water. Instead, they get the moisture they need from the plants they eat. This is possible due to their specially adapted digestive system, which breaks down plant fibers and extracts moisture more efficiently than other animals.

Biological Sciences to Room 9's Fantastic Fives website
Camels are specially adapted for life in the desert. Their body shape and physiology has adapted to suit the harsh environment. Over thousands and thousands.

Adaptation of camel 1
camel, (genus Camelus ), any of three species of large ruminating hoofed mammals of arid Africa and Asia known for their ability to go for long periods without drinking. The Arabian camel, or dromedary ( Camelus dromedarius ), has one back hump, while the domesticated Bactrian camel ( C. bactrianus) and the wild Bactrian camel ( C. ferus) have two.

Different anatomical adaptations in camel Download Scientific Diagram
Arabian camels have been domesticated for approximately 3,500 years and have been long valued as pack animals. They can carry large loads for up to 25 miles a day. Some cultures judge a person's.
Animal Adaptations Complete Guide Types of Animal Adaptation with Examples (2022)
Here are some of the primary behavioral adaptations of camels: Foraging and dietary habits: Camels are herbivores and can consume a wide variety of vegetation, including thorny plants, saltbushes, and grasses. They have adapted their foraging behavior to consume the available plant resources in their desert habitat.
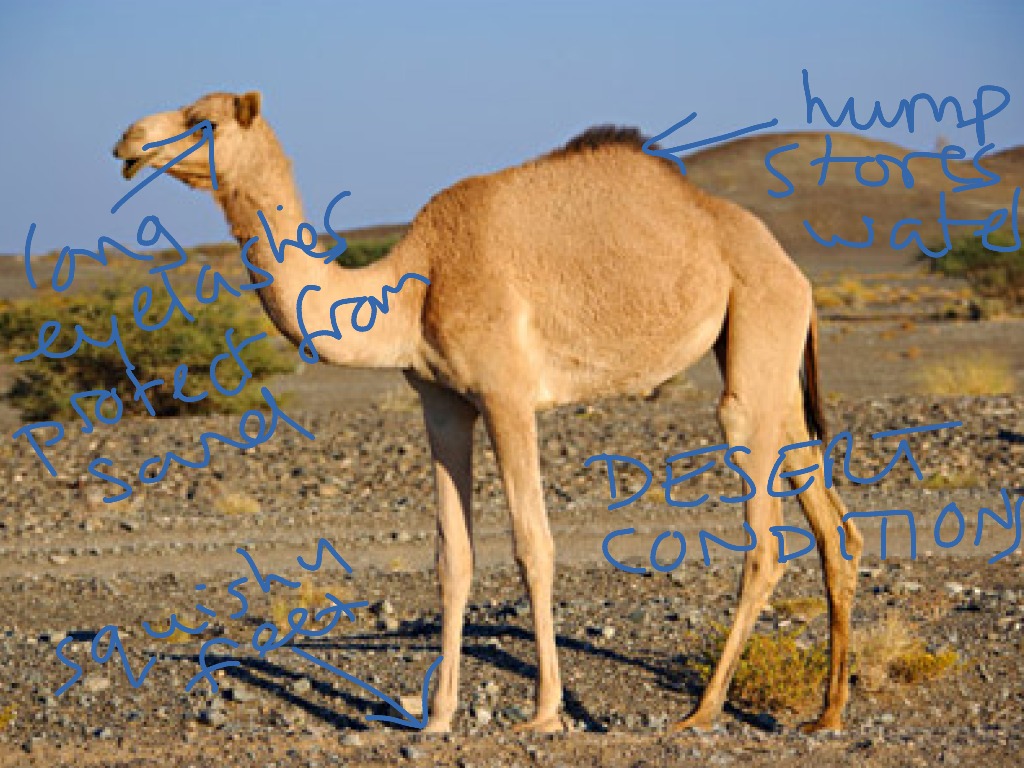

Camel adaptations Science ShowMe
Introduction The adaptability of animals to their environments is a remarkable phenomenon that continues to intrigue scientists and researchers alike. One of the most iconic examples of such adaptation is the camel's ability to survive and thrive in desert environments where resources are scarce and conditions are harsh.
camel_heat_regulation Wiki
When the camel is dehydrated, the kidneys reduce the loss of water by decreasing the rate of filtration while at the same time increasing the reabsorption of water. The loop of Henle in camels is about 4 to 6 times longer compared to cattle. Tolerance against water loss and water intake

Two Boys and a Dad Productions A Funny Thing Happened On the Way to a Research Project
One of the key adaptations that help wild camels survive changing weather patterns and temperature variations is their double coated fur. This unique adaptation allows these animals to regulate their body temperature more efficiently and stay warm during cold nights and cooler during hot days.

Camel adaptation Science, Biology, Evolution ShowMe
Camels have a series of physiological adaptations that allow them to withstand long periods of time without any external source of water. [23] The dromedary camel can drink as seldom as once every 10 days even under very hot conditions, and can lose up to 30% of its body mass due to dehydration. [24]

Pin on I Love Camels
Adaptations to windblown deserts include double rows of eyelashes, the ability to close the nostrils, and wide-spreading soft feet. They also can tolerate dehydration and high body temperatures. They are thus able to go several days without drinking water. Though docile when properly trained, camels can be dangerous.